LET’S FEEL NOW
In this video Professor Anne Phillips Co-Chair of iDEAL Diabetes CIC introduces why neuropathy and neuropathic pain are so important to recognise, diagnose and treat. The resources within this webpage are created to increase your knowledge and awareness of neuropathy and neuropathic pain presentations and treatments.
Mononeuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy can be divided into categories: mononeuropathy and polyneuropathy as images below show.
Mononeuropathy is damage to a single nerve or nerve group and is usually caused by injury. An example of a mononeuropathy is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). CTS affects the median nerve and is usually caused by repetitive motion of the hand and wrist. Other forms of mononeuropathy are axillary nerve dysfunction; peroneal nerve dysfunction; cranial mononeuropathy; femoral nerve dysfunction; ulnar nerve dysfunction and sciatic nerve dysfunction.
Mononeuropathies are localized to one area and can be treated with surgery, like carpal or cubital tunnel release surgery or a microdiscectomy for sciatic nerve dysfunction.
Polyneuropathy is the simultaneous malfunction of many peripheral nerves throughout the body (As the image above shows). Polyneuropathy can be acute or chronic. Acute cases can be caused by infections, toxins and certain drugs.
Chronic polyneuropathy can be caused by:
-
Diabetes,
-
Alcoholism,
-
Liver/ kidney failure or
-
Cancer.
While diabetes can cause diabetic neuropathy, peripheral neuropathy can occur in people who do not have diabetes. Certain types of cancer treatments and auto immune disorders (Sjogren’s syndrome, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Guillain-Barre syndrome) can cause chronic polyneuropathy.
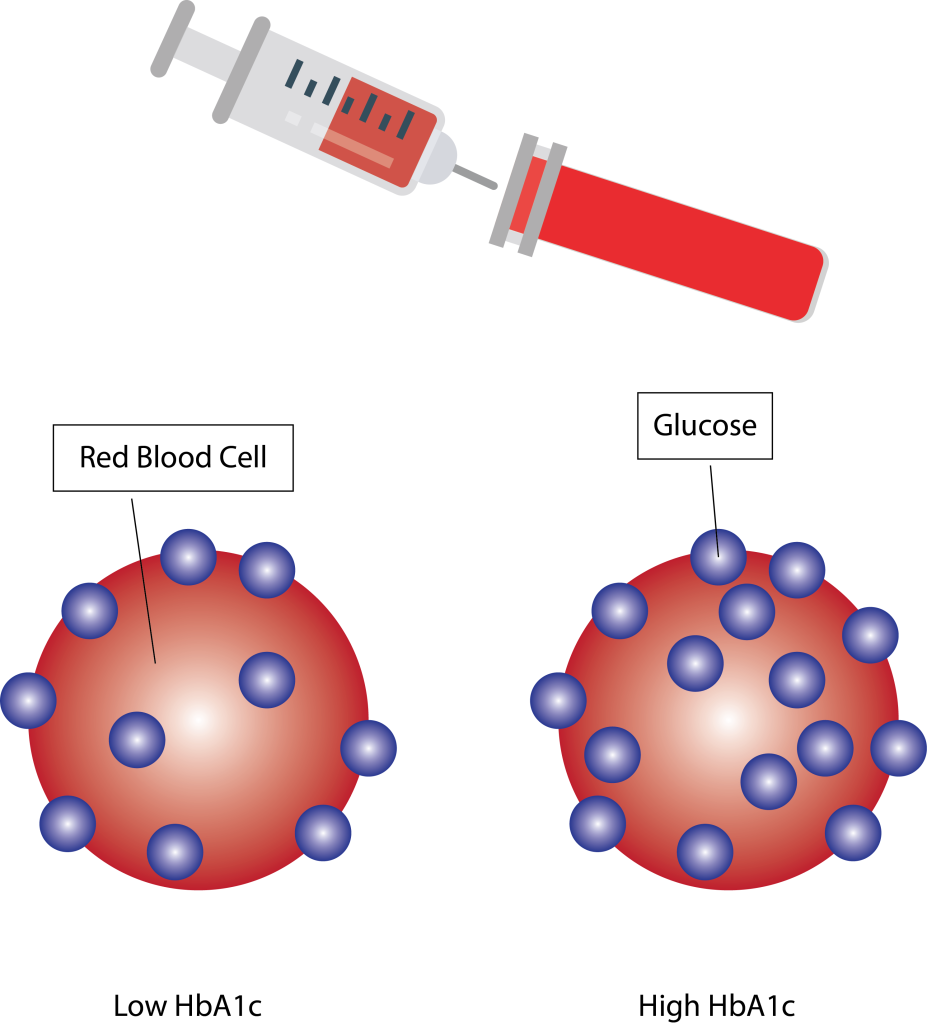
This image shows how high blood glucose over a proglonged period of time can cause an elevated Glycosylated Haemoglobin (HbA1c).
As the red blood cells are manufactured in the bone marrow, the percentage of glucose in the blood at the time of manufacture bines known as glycosylation onto the red blood cell for its life. The average red blood cell lasts 120 days. HbA1c is measured by a blood test which calculates the median percentage of glucose glycated onto the red blood cells. So it is a retrospective test, to assess glycaemic control, on average over the last 120 days.
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral: means Beyond (in this case, beyond the brain and the spinal cord)
Neuro-: means Related to the nerves
-pathy: means Disease
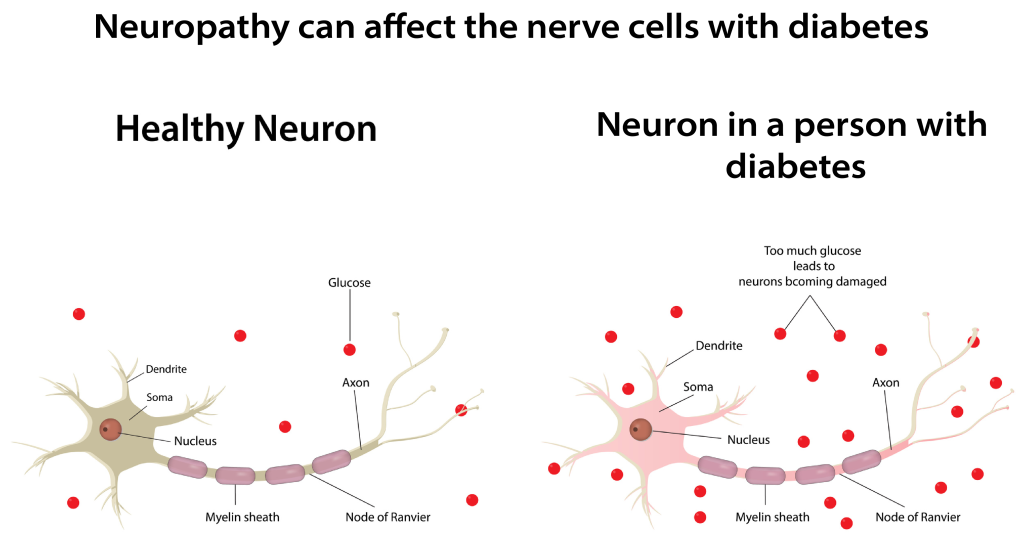
Peripheral neuropathy refers to the conditions that result when nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord from and to the rest of the body are damaged or diseased.
Neuropathy refers to damage to the nerves which makes them not function effectively. Peripheral neuropathy occurs when damage to nerves interrupts communication between the brain and other parts of the body. This can impair muscle movement, prevent normal sensation in the arms and legs, and cause neuropathic pain
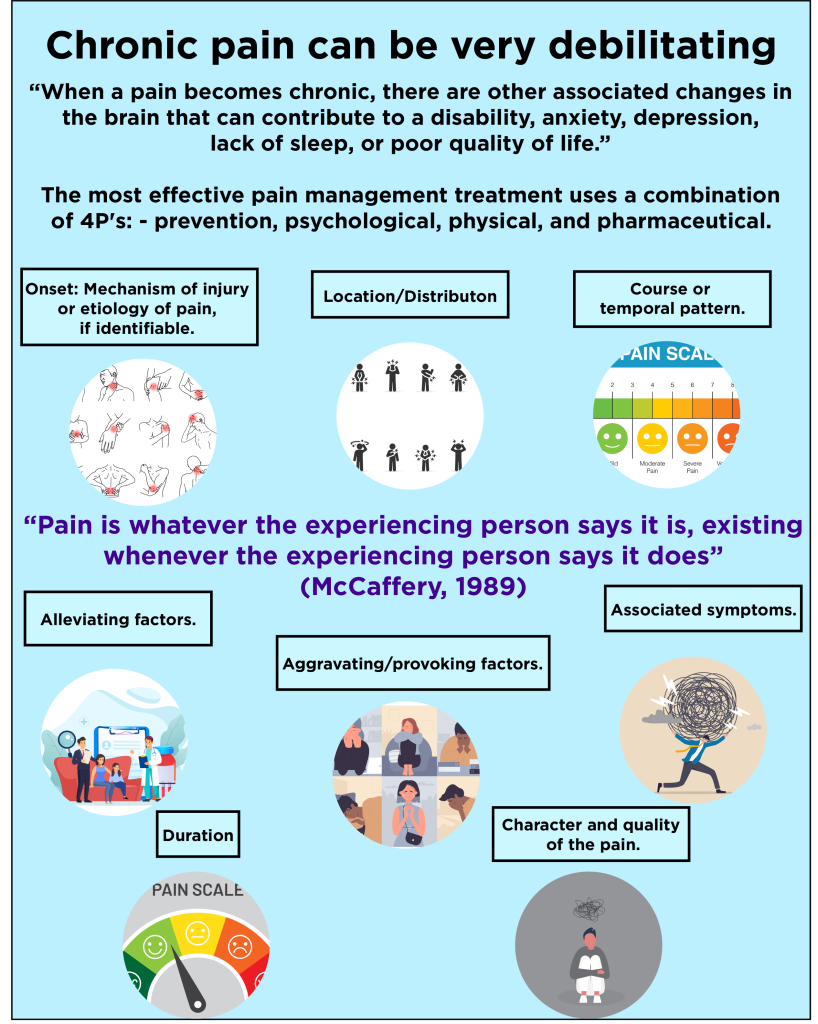
Here is a poster detailing LET’S FEEL NOW about Neuropathy and Neuropathic Pain
![Lets feel now [Recovered]](https://usercontent.one/wp/idealdiabetes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/Lets-feel-now-Recovered-697x1024.png?media=1687957852)
Neuropathic pain
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy and neuropathic pain depend on which nerves are affected. Numbness, tingling, burning pain, muscle weakness and paralysis can occur if the motor nerves have been affected. If autonomic nerves have been affected, heat intolerance, excessive sweating or inability to sweat, digestive problems or difficulties with blood pressure control can all be symptoms.
For many people, neuropathy can be reduced by treating the underlying cause.
For people with diabetes, improving HbA1c levels can help but, unfortunately, severe neuropathy can occur in people with well controlled HbA1c levels with diabetes also.
For others whose nerve damage comes from injury or has no underlying cause, the focus of treatment is to reduce pain and symptoms.
Usually an EMG (electromyography) which includes a nerve conduction study is used to diagnosis peripheral neuropathy.
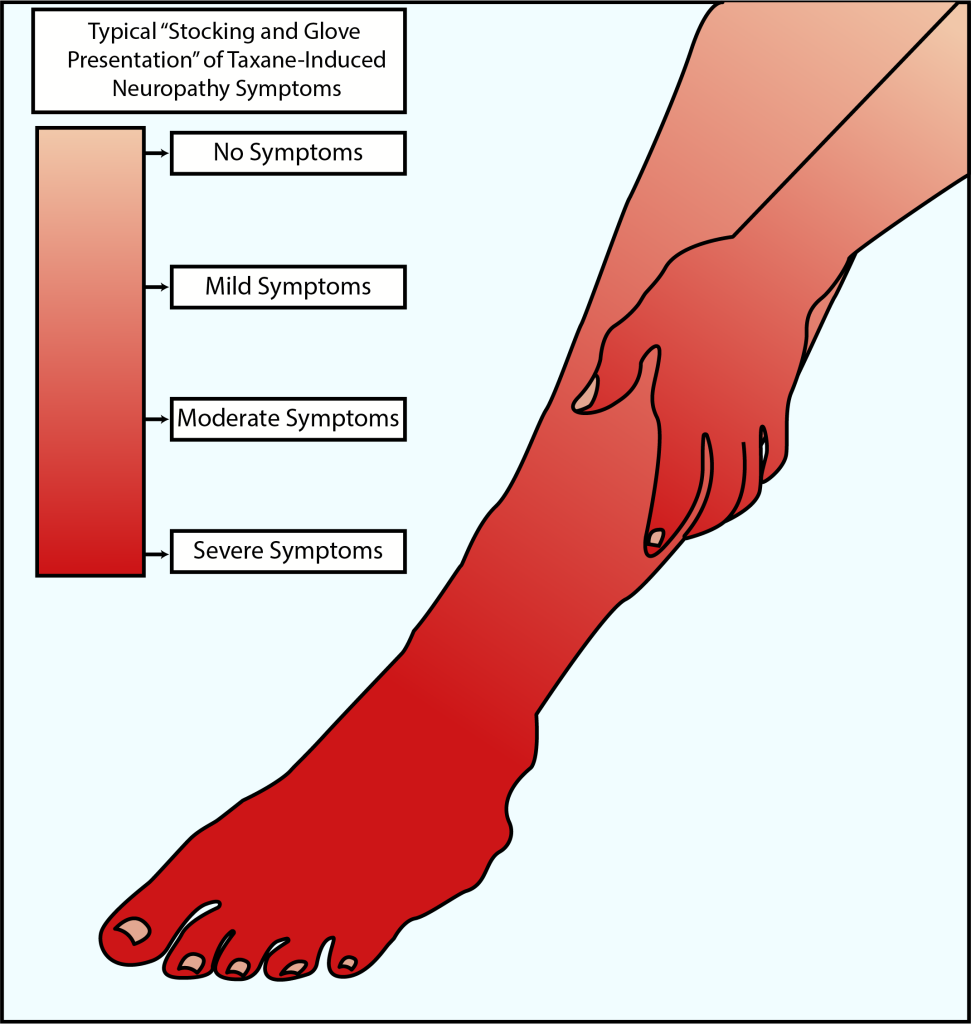
This image demostratres the typical peripheral foot and hand known as stocking and glove presentation of pain which affects the peripheral nerves which are furthest from the spinal colums first.
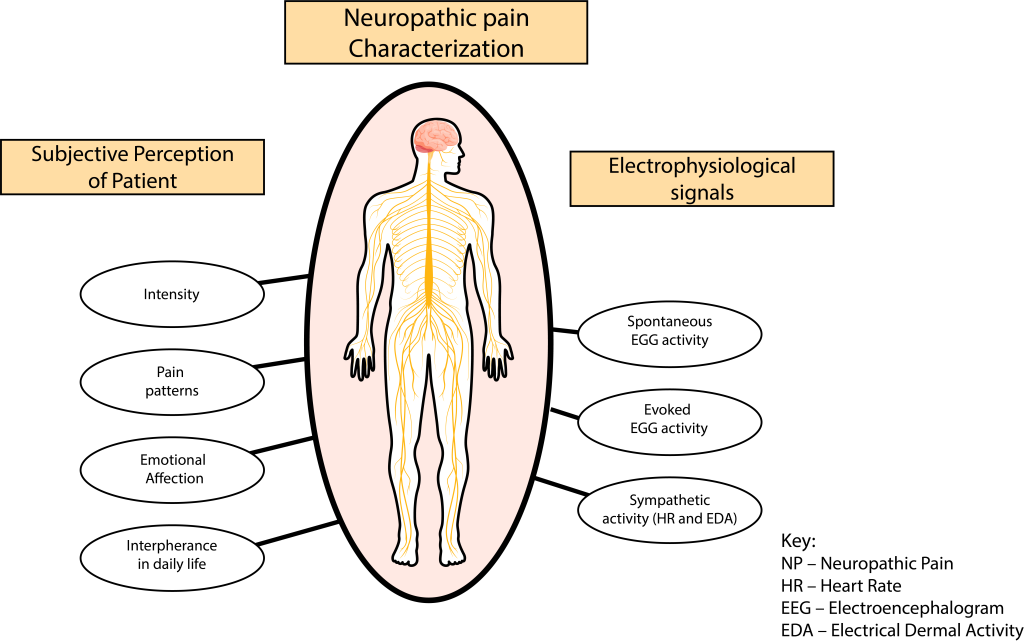
This image demonstrates how neuropathic pain can affect human beings internally and externally and emotionally. Living with neuropathic pain and can be an intensely distressing experience for many people.
Please watch this Optical illusion video which shows examples of what people with Neuropathic Pain can experience and describe. Each person is an individual and what health care professionals may assess as Neuropathic Pain can present very differently to the individual experiencing the pain. Like the images you see diffrent in this film you will see different things on first sight, the same is being experienced with Neuropathic pain and how it presents in each individual.
This poster illustrates how pain can manifest individually and very person affected, and therefore individual experiences need to be listened to and heard
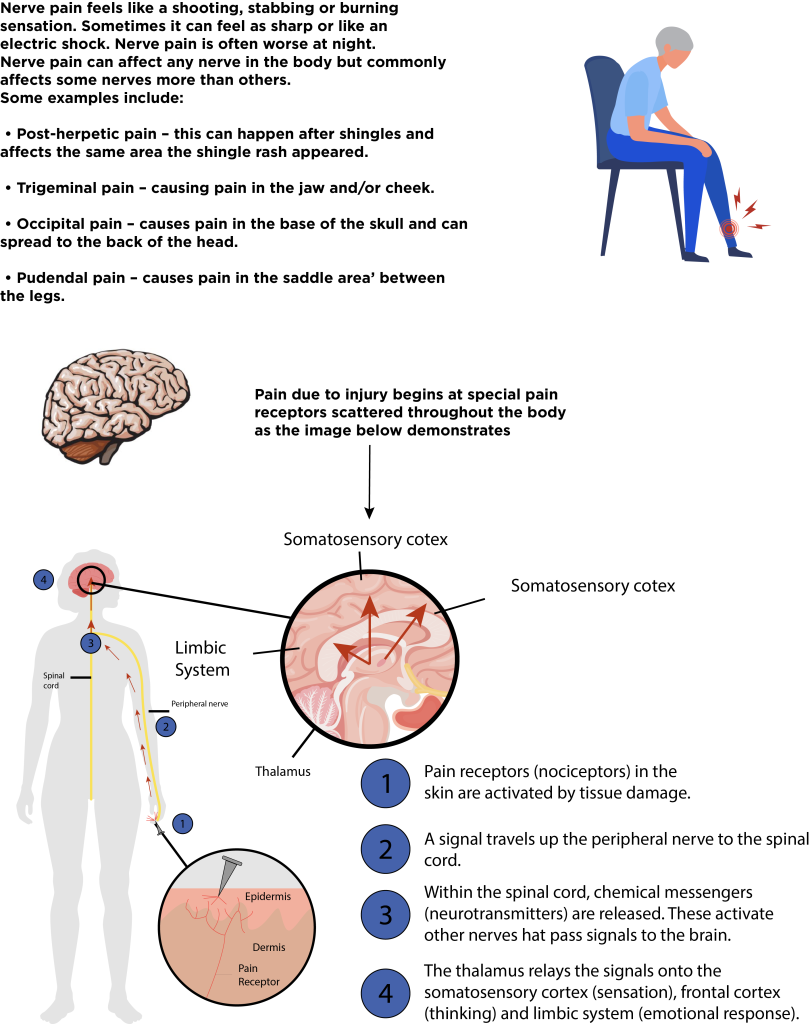
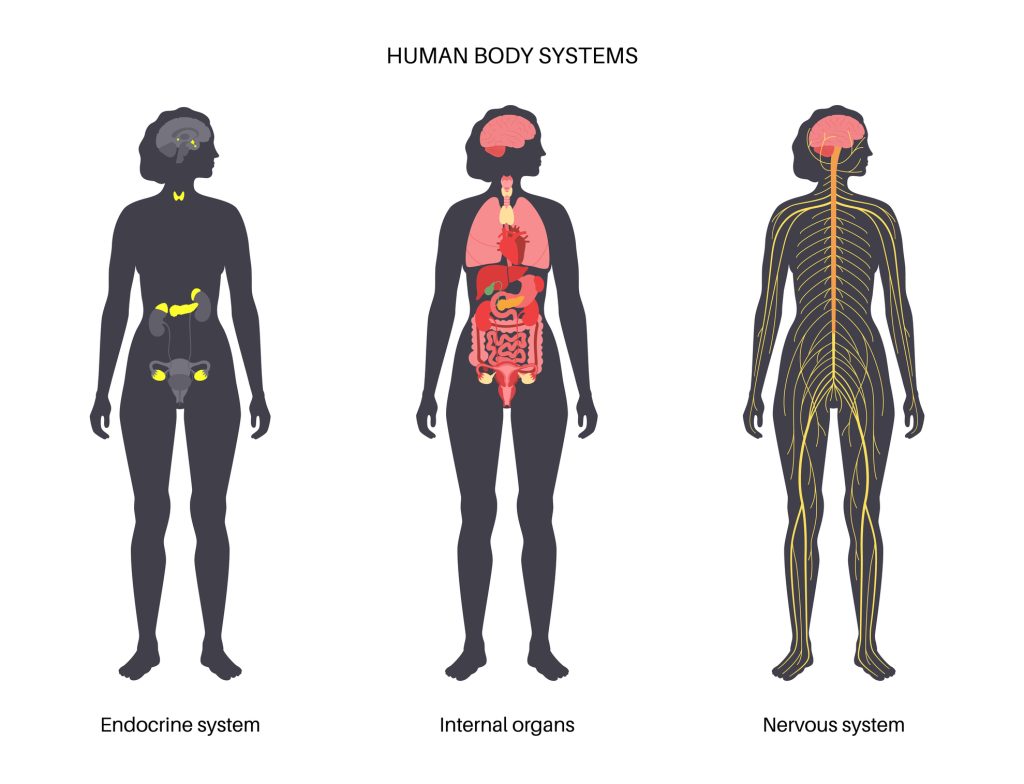
From the image above the nervous system has interplay with all the internal organs and as such if neuropathy is present then this can affect the functioning off the internal organs affected. Examples include internal organs such as the heart, blood vessels, digestive system, bladder, sweat glands, eyes, sex organs, heart rate and blood pressure, and the ability to feel symptoms of hypoglycaemia. Peripheral neuropathy affects the: Crennel Nerves which go from the brain to the eyes, mouth, ears, and other parts of the head. Peripheral nerves go from the spinal cord to the arms, hands, legs, and feet. Autonomic nerves go from the spinal cord to the lungs, heart, stomach, intestines, bladder, and sex organs. Central nerves are in the brain and spinal cord.
Multi-disciplinary Health Care Professionals who work with People with diabetes at risk of or experiencing Neuropathic Pain
These examples of feedback were gathered from people each of whom have or are experiencing neuropathic pain
![Qoutes [Recovered]](https://usercontent.one/wp/idealdiabetes.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/Qoutes-Recovered-949x1024.png?media=1687957852)
This LET’S FEEL NOW Project Webpage and contents has been created by an independent Multi-Disciplinary Team. Viatris provided unrestricted educational grant for the development and production of this webpage but has had no input into the content.











